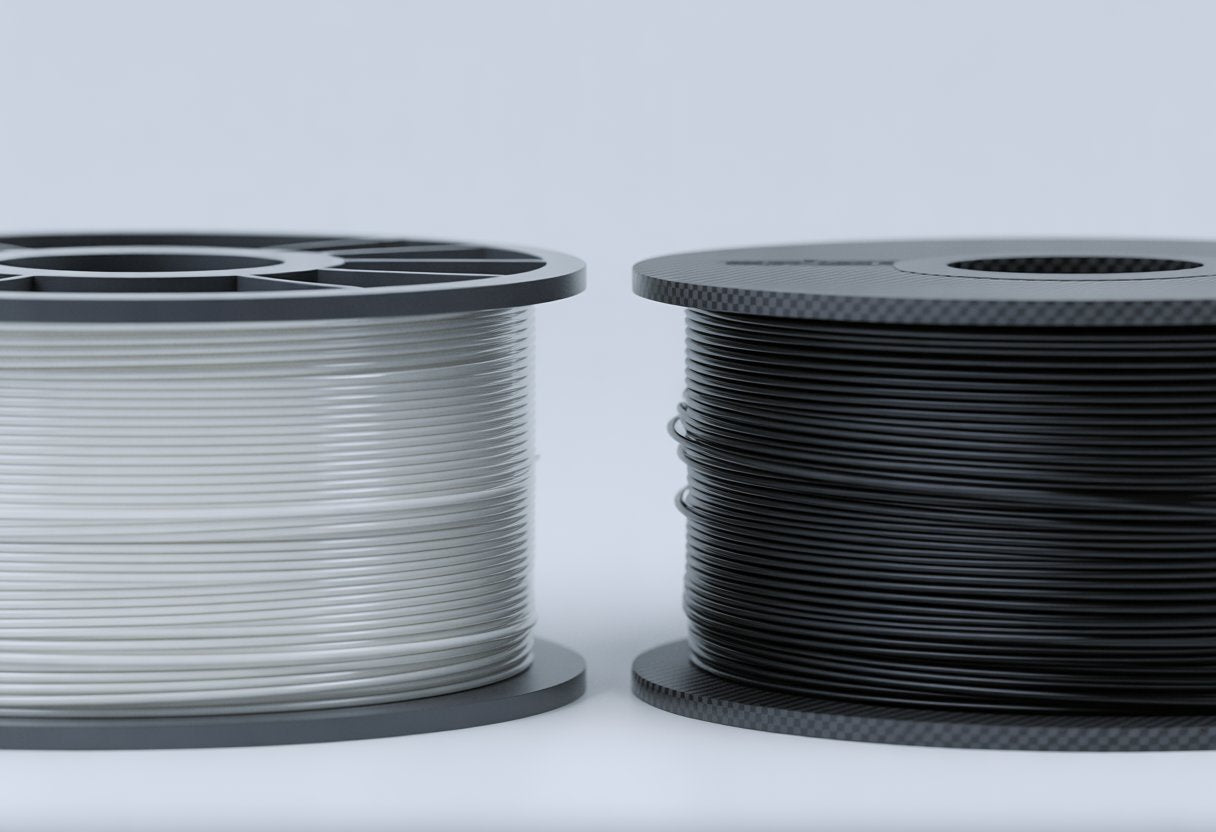
PETG HF vs CF can be confusing when you want strong, clean prints fast. PETG HF, or high-flow PETG, focuses on speed and smooth printing.
PETG CF, or carbon fiber PETG, gives you more strength and stiffness for tough parts.
You’ll notice PETG HF prints easier and faster, but it may lose a bit of strength. PETG CF takes longer to print but gives better heat resistance and durability.
Key Takeaways
- PETG HF prints faster with smoother surfaces.
- PETG CF offers higher strength and stiffness.
- Choosing the right one depends on speed or durability needs.
Compare it with other popular materials in our guide, PETG vs PLA: Which Filament Is Best for 3D Printing?
Summary Table: PETG-HF vs PETG-CF 3D Printing Filaments
|
Category |
PETG-HF (High Flow) |
PETG-CF (Carbon Fiber Reinforced) |
|
Base Material |
PETG |
PETG |
|
Additive |
Flow enhancers |
Short carbon fibers |
|
Structure |
Homogeneous polymer |
Fiber-reinforced composite |
|
Primary Benefit |
Faster printing and smoother flow |
Higher stiffness and strength |
|
Print Speed |
Very fast (up to 150–200 mm/s) |
Moderate (60–100 mm/s) |
|
Strength |
Moderate |
High |
|
Toughness / Flexibility |
High / Slightly flexible |
Lower / Rigid |
|
Stiffness |
Medium |
Very high |
|
Impact Resistance |
Good |
Moderate |
|
Heat Resistance (HDT) |
~70–80°C |
~85–90°C |
|
Surface Finish |
Glossy, smooth |
Matte, textured |
|
Visual Appeal |
Shiny, clean look |
Professional, understated finish |
|
Nozzle Type |
Standard brass or hardened steel |
Hardened steel or ruby (abrasive) |
|
Abrasion Risk |
Low |
High |
|
Ease of Printing |
Easy, high-flow optimized |
Moderate, slower extrusion |
|
Layer Adhesion |
Excellent |
Strong but may need higher temps |
|
Warping Tendency |
Low |
Low to moderate |
|
Best For |
Prototypes, fast prints, large parts |
Functional, load-bearing, heat-resistant parts |
|
Ideal Applications |
Tools, jigs, visual models |
Brackets, mounts, automotive, engineering parts |
|
Overall Advantage |
Speed and smoothness |
Strength, rigidity, and heat stability |
PETG HF vs CF: Key Differences

You get faster printing and smoother flow with PETG HF. PETG CF gives stronger, stiffer parts.
Material Composition and Structure
PETG HF is a high-flow version of standard PETG. It melts and moves through the nozzle more easily, letting you print faster without losing layer bonding. The formula focuses on improving flow and layer adhesion.
PETG CF, or carbon fiber–reinforced PETG, mixes short carbon fibers into the base PETG. These fibers add stiffness and reduce warping.
The carbon fibers don’t melt; they stay solid inside the plastic, creating a composite material that’s both light and rigid.
|
Property |
PETG HF |
PETG CF |
|
Base Material |
PETG |
PETG |
|
Additive |
Flow enhancers |
Carbon fiber |
|
Structure |
Homogeneous polymer |
Fiber-reinforced composite |
|
Key Benefit |
Faster printing |
Higher stiffness |
PETG CF can be abrasive, so you need a hardened nozzle. PETG HF prints fine with standard brass nozzles.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
PETG HF keeps the flexibility and toughness of regular PETG. It can handle bending and impact without cracking.
PETG CF trades some toughness for strength and stiffness. The carbon fibers carry loads better, giving parts higher rigidity and less flex. The added fibers make it more brittle under sudden impact.
|
Property |
PETG HF |
PETG CF |
|
Strength |
Moderate |
High |
|
Toughness |
High |
Lower |
|
Stiffness |
Medium |
Very high |
|
Impact Strength |
Good |
Moderate |
If you need parts that flex slightly, go with PETG HF. If you need firm, load-bearing parts, PETG CF performs better.
Heat Resistance and HDT
PETG HF keeps a heat deflection temperature (HDT) similar to standard PETG, usually around 70–80°C. It softens under higher heat but stays stable for most indoor or light mechanical uses.
PETG CF improves heat resistance slightly. The carbon fibers help the part hold its shape better at higher temperatures, often pushing the HDT closer to 85–90°C. The fibers don’t expand as much as plastic, which helps reduce warping when parts heat up.
Surface Finish and Appearance
PETG HF prints with a glossy, smooth surface. It shows clear layer lines but can look shiny and clean. The material’s flow helps reduce stringing and blobs, giving a neat finish.
PETG CF has a matte, textured surface. The carbon fibers scatter light, hiding layer lines and giving a professional look. The texture also helps mask small printing flaws.
|
Property |
PETG HF |
PETG CF |
|
Finish |
Glossy |
Matte |
|
Texture |
Smooth |
Slightly rough |
|
Visual Appeal |
Shiny |
Professional look |
You’ll notice PETG CF feels lighter and more rigid in hand. PETG HF feels smoother and slightly flexible.
For heat‑resistant projects, check out the Heat Resistant Filament Collection.
3D Printing Considerations

When printing with PETG-HF or PETG-CF, you need to think about nozzle wear, print speed, and how layers stick together. Each material behaves differently and needs small changes in your setup to get clean, strong prints.
Nozzle Requirements and Material Abrasion
PETG-CF has carbon fibers mixed into the filament, which makes it more abrasive. These fibers can wear down a brass nozzle fast. You should use a hardened steel or ruby-tipped nozzle to keep print quality consistent.
PETG-HF is not abrasive, so a standard brass nozzle works fine. It benefits from a clean nozzle since the faster flow rate can clog small openings.
|
Material |
Recommended Nozzle |
Abrasion Risk |
|
PETG-HF |
Brass or Hardened Steel |
Low |
|
PETG-CF |
Hardened Steel or Ruby |
High |
Keep your nozzle temperature around 240–260°C for both, but check the manufacturer’s guide. PETG-CF may need slightly higher heat to maintain smooth extrusion.
Print Speed and Settings
PETG-HF is made for high-flow printing, so you can print faster without losing much detail. It works well for large parts or when you want to shorten print time. You might reach speeds of 150–200 mm/s depending on your printer’s power.
PETG-CF prints slower because the fibers reduce flow and increase nozzle wear. Try speeds between 60–100 mm/s for better layer bonding and surface finish.
Use a 0.4–0.6 mm nozzle and 0.2–0.3 mm layer height for balanced results. Slower cooling fans help both materials keep good layer adhesion and reduce stringing.
Layer Adhesion and Warping
PETG-HF sticks well between layers and rarely warps, even on large prints. It’s good for parts needing smooth walls and dimensional stability. Drying the filament before use helps prevent bubbles or weak spots.
PETG-CF has stronger stiffness but can show small gaps between layers if printed too cold. Keep the bed at 70–80°C and use an enclosure if possible.
For both materials, clean the build plate and use a light adhesive like glue stick or PEI sheet. This keeps edges from lifting and improves first-layer grip.
Learn more about PETG’s performance in our article, What Is PETG Filament: A Guide in 3D Printing Applications.
Best Use Cases for PETG HF and CF
You can get strong, heat-resistant parts with PETG CF. PETG HF gives you faster prints and smoother surfaces.
Mechanical Components and Structural Parts
When you print mechanical components or structural parts, PETG CF often performs better. The carbon fiber adds stiffness and reduces flex, which helps parts hold their shape under stress. You can use it for brackets, mounts, gears, and frames that need to stay rigid.
PETG HF prints faster and still keeps decent strength. It’s a good choice for prototypes or low-load parts where speed matters more than maximum strength.
|
Property |
PETG HF |
PETG CF |
|
Print Speed |
Faster |
Moderate |
|
Rigidity |
Medium |
High |
|
Impact Resistance |
Good |
Very Good |
|
Surface Finish |
Smooth |
Matte, textured |
If you need to test designs quickly, start with PETG HF. For the final version that must last, switch to PETG CF.
Automotive Parts and Engineering Applications
PETG CF stands out for automotive and engineering uses where heat resistance and tensile strength are key. You can print dash mounts, clips, housings, or small engine covers that face vibration and mild heat.
The carbon fibers help the part resist warping and hold tight tolerances. PETG HF works well for tooling, jigs, and fixtures that don’t face high heat. It’s easier to print and gives a cleaner look.
You can also anneal PETG CF parts after printing to improve strength and temperature resistance even more.
If your project involves load-bearing or precision-fit parts, PETG CF is the safer pick. For quick prototypes or cosmetic pieces, PETG HF saves time.
Selecting the Right Filament for Your Project
Choose based on what matters most: speed, strength, or durability. PETG HF gives you faster prints with fewer moisture issues when dried properly.
PETG CF gives you higher stiffness and better heat handling, but it can wear nozzles faster and needs careful drying.
Ask yourself:
- Do you need impact resistance or fine detail?
- Will the part face heat or stress?
- Are you printing one-off parts or production runs?
If you print often and need parts that last, PETG CF is worth the extra care. For everyday prints or design testing, PETG HF keeps things simple and efficient.
If flexibility matters, try the Flex TPU Filament for 3D Printing Collection.
Alternative PETG Composites
You can find other PETG mixes that trade a bit of flexibility for better strength, heat resistance, or print speed. These blends use fibers or additives to boost performance for parts that face stress, heat, or wear.
PETG-GF: Glass Fiber Reinforced PETG
PETG-GF mixes glass fibers into regular PETG to make a tougher composite material. The glass fibers increase stiffness and reduce warping, which helps when printing large or flat parts.
You’ll notice that it feels more rigid than plain PETG but less brittle than carbon fiber blends. It also keeps a cleaner surface finish and resists heat slightly better.
|
Property |
PETG |
PETG-GF |
|
Stiffness |
Medium |
High |
|
Flexibility |
Moderate |
Low |
|
Heat Resistance |
Good |
Better |
|
Print Difficulty |
Easy |
Moderate |
Dry the filament before printing to avoid bubbles or rough texture. You may need a hardened nozzle since glass fibers can wear down brass quickly.
Other Specialty PETG Blends
Some PETG variants include PETG-HF (high flow) for faster printing, PETG-ESD for static-safe parts, and PETG-CF for high stiffness. Each version changes how the filament melts, flows, or cools.
- PETG-HF helps you print quicker without losing much detail.
- PETG-ESD protects electronics by reducing static buildup.
- PETG-CF adds carbon fibers for light but strong components.
Experience top-tier strength and stiffness with the PETG-CF Filament Collection.
Bottom line
When comparing PETG-HF vs PETG-CF, the choice depends on your project’s priorities. PETG-HF (high flow) offers faster printing speeds and smoother layer adhesion, making it ideal for prototypes and large prints.
PETG-CF (carbon fiber reinforced) delivers superior stiffness, dimensional stability, and heat resistance—perfect for functional, load-bearing parts. Both materials excel in durability and print quality, but PETG-CF edges ahead for performance applications.
Whether you prioritize speed or strength, selecting the right filament ensures optimal results.
For premium-quality PETG and PETG-CF options, check out Siraya Tech’s filaments and elevate your 3D printing projects.
See how to optimize your printing results by checking out our article: Mastering Flexible Filament Printing on Creality K1, K1C.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the main difference between HF and CF PETG filaments?
PETG HF stands for high flow, which means it moves through the nozzle faster and can print quicker. PETG CF adds carbon fiber, making it stronger and more rigid but also more abrasive on the nozzle.
How does the strength of PETG HF compare to PETG CF?
PETG CF is tougher and more rigid because of the carbon fiber. PETG HF is still strong but focuses more on speed and smoothness.
You’ll notice CF parts flex less and hold shape better under stress.
Can you break down the print settings for PETG HF and CF?
PETG HF prints best at higher speeds and slightly higher flow rates. Keep the nozzle around 250°C and bed around 75°C.
PETG CF needs a hardened steel nozzle, slower speeds, and similar temps. Dry both filaments before use for cleaner prints.
What are the best uses for PETG HF in 3D printing?
Use PETG HF when you want fast prints with good detail and strength. It’s great for prototypes, models, and parts that don’t need extreme stiffness.
How does CF PETG hold up against heat compared to HF?
PETG CF handles heat better thanks to the carbon fiber. It keeps its shape at higher temps than PETG HF, which can soften a bit sooner under heat.
What's the deal with the surface finish of PETG CF vs. HF?
PETG CF has a matte finish that hides layer lines and looks more professional. PETG HF has a glossier surface that shows more detail but also more shine.